The work of George Lindsay is predominately concerned with timing turns in the market but he did have at least one method of forecasting price. Specifically, forecasting bear market lows following 3PDh formations. He called this approach the Tri-Day Method and explained it in a series of five supplements to his newsletter from May to September 1959.
This method forecast a low to the 1917 bear market of 65.85. The actual low on December 19, 1917 was 65.95.
It forecast a low in the post-1929 bear market of 41.75. The actual low on July 7, 1932 was 41.22.
It forecast a low to the correction in 1953 of 256.32. The actual low on September 14, 1953 was 255.49.
While it would not make a material difference in forecasting the low of our new bear market, the realization that the 2012-2013 3PDh formation is a hybrid Lindsay called Model 3 explains why I didn’t recognize the pattern earlier. In Model 3 the reaction following peak 3 becomes the First Floor Roof of the pattern. The reaction following peak 3 on October 5, 2012 clearly breaks down into five waves – the most important requirement of a First Floor Roof. A First Floor Roof taking the place of the Separating Decline (reaction following peak 3) is a defining characteristic of Model 3.
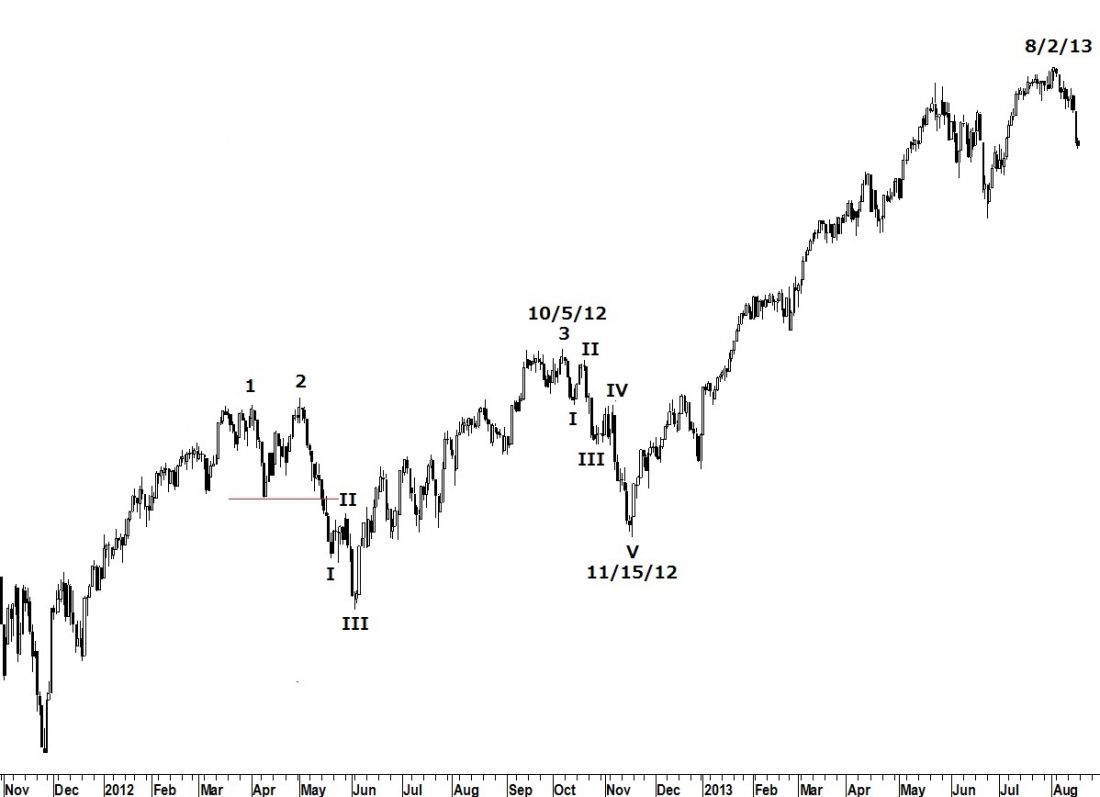
Let’s examine a check list for recognizing Model 3:
- The decline following peak 2 is composed of three waves – check!
- The low of the reaction following peak 2 is lower than the reaction following peak 1 – check!
- Peak 3 is the highest point of the three peaks – check!
- The reaction following peak 3 holds above the reaction following peak 2 – check!
Once the model is identified we can use the Tri-Day Method to develop a forecast for the low of the bear market.
The distance from the closing high of peak 3 on October 5, 2012 to the low on 11/15/12 is 1,068 Dow points.
The distance from the low on 11/15/12 to the high of the Domed House on August 2, 2013 is 3,116 Dow points.
The swingover ratio is 3,116/1,068 and equals 2.90. While the ratio is typically limited to 2.0 (regardless of its determined value), when the distance between the highest peak and the high of the Domed House is 10 months or greater (as it is now) the ratio is capped at 2.2.
The expected loss in the Dow is calculated as follows.
3,116 x 2.2 =6,855
6,855 – 1,068 =5,787
5,787 Dow points is the expected minimum loss for the Dow Industrials index.
Subtracting 5,787 from the high, 15,658, provides a forecast for the Dow of 9,871.
3PDh and the Tri-Day Method are explained, in detail, in the book George Lindsay and the Art of Technical Analysis -FT Press, 2011.
Who was George Lindsay? Learn more about his analysis here: Seattle Technical Advisors.